In today’s health-conscious world, many individuals are exploring alternative diets such as gluten-free or vegan options. These dietary choices have gained popularity due to their potential benefits, including improved digestive health, weight management, and reduced risk of various diseases. Whether you are looking to adapt to a gluten-free lifestyle or embrace veganism, understanding the advantages of these diets can help you make informed decisions about your own health and well-being.

Gluten-free Diet
A gluten-free diet is becoming increasingly popular for various reasons. One of the main benefits is relief from digestive issues. Many individuals experience discomfort, bloating, and diarrhea after consuming foods containing gluten. By eliminating gluten from your diet, you may find relief from these symptoms and improve your overall digestion.
In addition to improved digestion, a gluten-free diet can also lead to improved energy levels. For individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, consuming gluten can cause fatigue and brain fog. By eliminating gluten, you may experience increased energy and mental clarity.
Reduced inflammation is another advantage of following a gluten-free diet. Gluten is known to trigger inflammation in individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. By avoiding gluten-containing foods, you may reduce inflammation in your body and experience various health benefits.
For individuals with celiac disease, a gluten-free diet is essential for managing their condition. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that damages the small intestine when gluten is consumed. Following a gluten-free diet is crucial for preventing further damage and managing symptoms associated with this condition.
Lastly, a gluten-free diet may potentially promote weight loss. Many gluten-containing foods are high in calories and carbohydrates. By effectively eliminating these foods from your diet, you may reduce your calorie intake and lose weight.
Vegan Diet
A vegan diet is characterized by the exclusion of all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey. This diet offers a range of benefits for your health and well-being.
Improved heart health is one of the most significant advantages of following a vegan diet. Plant-based foods are typically low in saturated fats and cholesterol, reducing the risk of heart disease and high blood pressure. By opting for a vegan diet, you can protect your heart and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
Additionally, a vegan diet is associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases. Studies have shown that individuals who follow a vegan diet have a lower risk of developing conditions such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and obesity. This is attributed to the higher intake of plant-based foods that are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Weight management is another benefit of a vegan diet. Plant-based foods tend to be lower in calories and fat compared to animal products. By focusing on a diet centered around fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, you can maintain a healthy weight or potentially lose weight if needed.
Increasing your intake of fruits and vegetables is an essential aspect of a vegan diet. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, providing your body with essential nutrients and promoting overall health. By consuming a wide variety of colorful plant foods, you can boost your immune system and improve your overall well-being.
Aside from the personal health benefits, a vegan diet also considers ethical and environmental considerations. By choosing to avoid animal products, you are making a positive impact on animal welfare and reducing your carbon footprint. This aspect of a vegan lifestyle resonates with individuals who are passionate about sustainability and creating a more compassionate world.

Gluten-free vs. Vegan Diets
Both gluten-free and vegan diets share some similarities in terms of excluding specific food items but have distinct differences in the types of foods avoided.
When it comes to the health implications, both diets offer benefits. A gluten-free diet can provide relief from digestive issues, improved energy levels, and reduced inflammation. On the other hand, a vegan diet offers features such as improved heart health, reduced risk of chronic diseases, weight management, and increased intake of fruits and vegetables.
Suitability for individuals with specific conditions varies between gluten-free and vegan diets. A gluten-free diet is essential for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, as consuming gluten can cause significant health issues. On the other hand, a vegan diet may not be suitable for individuals with certain nutrient deficiencies or certain medical conditions requiring animal-based food sources.
Nutritional considerations play a crucial role in both diets. A gluten-free diet requires careful monitoring to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients that may be lacking due to the exclusion of gluten-containing foods. Similarly, a vegan diet requires attention to specific nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are primarily found in animal products.
Both gluten-free and vegan diets can pose potential challenges. Living a gluten-free lifestyle may involve careful label reading to identify hidden sources of gluten. Similarly, following a vegan diet may require planning to obtain all essential nutrients and finding suitable substitutes for animal-based products.
Gluten-free and Vegan Options
For individuals following a gluten-free diet, there are a variety of gluten-free alternatives available. These include gluten-free grains such as quinoa, rice, millet, and amaranth. Gluten-free flours like almond, coconut, and tapioca flour can be used for baking. Additionally, there are gluten-free pasta options made from rice, corn, or legumes.
Vegan substitutes for animal-based products have become readily available in recent years. For those seeking alternatives to meat, options include tofu, tempeh, seitan, and various plant-based meats made from ingredients like soy, wheat, or pea protein. Dairy substitutes include almond milk, soy milk, oat milk, and coconut milk. Vegan cheese, made from nuts or soy, is also a popular choice.
When following a gluten-free or vegan diet, it is important to be aware of common ingredients to avoid. Gluten-containing ingredients include wheat, barley, rye, and their derivatives. For a vegan diet, ingredients to avoid include meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, and honey. Reading labels and being knowledgeable about ingredient lists is essential when shopping for gluten-free and vegan products.
Cooking and dining out can be enjoyable experiences while following a gluten-free or vegan diet. When cooking, try experimenting with new flavors and ingredients to keep your meals exciting and delicious. When dining out, many restaurants now offer gluten-free and vegan options on their menus. Additionally, communicating your dietary needs to the staff can ensure a safe and enjoyable dining experience.
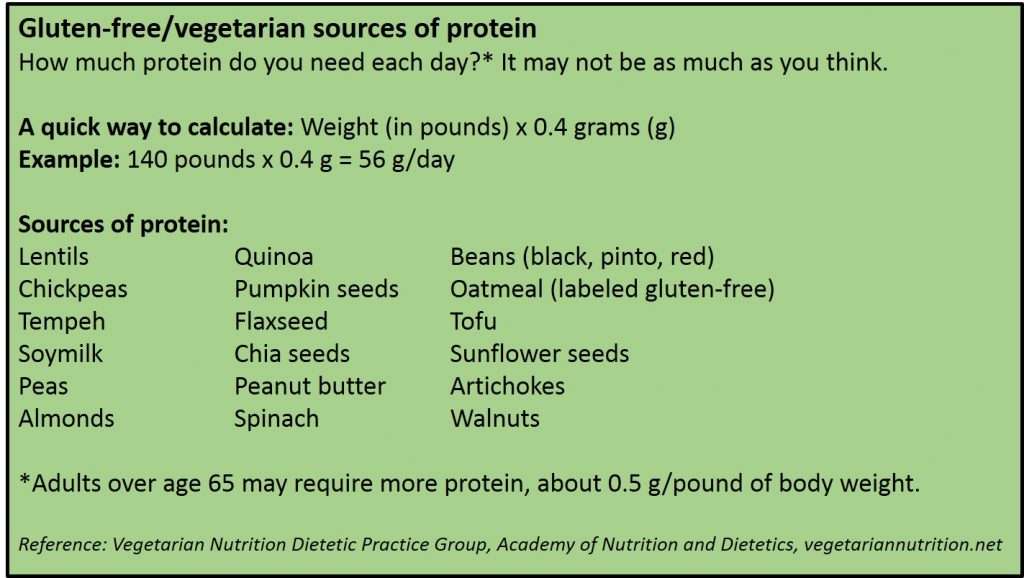
Cautionary Considerations
While there are many benefits to gluten-free and vegan diets, it is important to be mindful of potential pitfalls and challenges.
Unintended nutritional deficiencies can occur in both diets if not properly planned. Individuals on a gluten-free diet may be at risk of inadequate intake of certain vitamins, minerals, and fiber due to the exclusion of gluten-containing grains. Similarly, individuals following a vegan diet need to ensure they are obtaining sufficient amounts of key nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Processed gluten-free and vegan products may also pose a challenge. While there are many naturally gluten-free and vegan whole foods available, there is a wide range of processed products on the market that may not be as nutritious. These products often contain high amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives. It is important to read labels and choose whole, minimally processed options whenever possible.
Social challenges and support can also play a role in following a gluten-free or vegan diet. Attending social events or eating out with friends and family may require additional planning, communication, and understanding. Seeking support from like-minded individuals or joining online communities can be beneficial for sharing experiences, tips, and advice.
Importance of seeking professional guidance cannot be stressed enough. Consulting with healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians or nutritionists, can provide valuable guidance and ensure your dietary needs are met. They can assess your individual requirements, develop a personalized plan, and monitor your health to prevent any potential deficiencies or complications.
Gluten-free and Vegan Diet for Weight Loss
Both gluten-free and vegan diets have been associated with potential weight loss benefits. However, it is important to approach weight loss in a healthy and sustainable manner.
The effectiveness of a gluten-free or vegan diet for weight loss varies depending on individual factors such as overall calorie intake, physical activity levels, and individual metabolism. While eliminating gluten or animal products may result in weight loss for some individuals, it is essential to focus on balanced meal planning and portion control. Incorporating a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, can provide the necessary nutrients and keep you feeling satisfied.
In addition to dietary changes, regular exercise and physical activity are important for weight management. Combining a gluten-free or vegan diet with regular exercise can help to increase caloric expenditure, build muscle, and improve overall fitness. Including a mix of cardiovascular exercise and strength training can provide optimal results.
Sustainability and long-term success should be key considerations when embarking on a weight loss journey. Both gluten-free and vegan diets can be sustainable if approached with a balanced and varied approach. It is important to listen to your body, incorporate variety, and focus on overall health rather than solely weight loss.
Considerations for different body types should also be taken into account. Not all bodies respond the same way to specific diets. Each individual has unique needs and preferences, and it is important to find an approach that suits your body type and lifestyle. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.

Impact of Gluten-free and Vegan Diets on Gut Health
Following a gluten-free or vegan diet can have a significant impact on gut health.
Evidenced benefits on the gut microbiome have been observed in individuals following a gluten-free diet. Consuming gluten can trigger inflammation and disrupt the balance of gut bacteria in individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. By eliminating gluten, the gut microbiome can restore its balance, leading to improved digestion and overall gut health.
Similarly, a vegan diet has the potential for improved digestion. Plant-based foods are rich in fiber, which can promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. The increased intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provides prebiotics, which are essential for the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
The effect of gluten-free and vegan diets on gut-related conditions may vary. Individuals with conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may experience relief by eliminating gluten or animal products from their diet. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate dietary approach for these conditions.
Maintaining a diverse diet is essential in both gluten-free and vegan diets. Variety is key to obtaining a wide range of nutrients and promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Including a variety of gluten-free grains, vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, and seeds ensures you are receiving a broad spectrum of beneficial compounds and essential nutrients.
Individual variability should be considered when it comes to gut health and diet. Each individual has a unique gut microbiome and dietary needs. What works for one person may not work for another. It is important to listen to your body, pay attention to any digestive symptoms, and make adjustments to your diet accordingly.
Gluten-free and Vegan Diets during Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a crucial time for proper nutrition, and special considerations must be taken for those following gluten-free or vegan diets.
Ensuring nutritional adequacy is of utmost importance during pregnancy, regardless of dietary restrictions. For those following a gluten-free diet, it is essential to focus on obtaining necessary nutrients such as folate, iron, and calcium from alternative sources. Incorporating gluten-free grains, leafy greens, legumes, and iron-rich foods can help meet these needs.
For pregnant individuals following a vegan diet, it is important to ensure sufficient intake of nutrients that are commonly found in animal products. This includes vitamin B12, iron, calcium, omega-3 fatty acids, and iodine. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide guidance on appropriate supplementation or alternative food sources to meet these nutritional needs.
Monitoring potential deficiencies is crucial during pregnancy. Regular blood tests can help assess levels of key nutrients and identify any deficiencies that may need to be addressed. Working closely with a healthcare professional throughout your pregnancy can help ensure your dietary needs are met and any concerns are addressed in a timely manner.
The impact of a gluten-free or vegan diet on fetal development should also be considered. With proper planning and attention to balanced nutrition, both diets can support a healthy pregnancy. However, it is important to work with a healthcare professional to ensure that all nutritional needs are being met to support optimal growth and development of the baby.
Consultation with healthcare professionals is vital for pregnant individuals following a gluten-free or vegan diet. They can provide specialized advice and help create a personalized meal plan to ensure nutritional adequacy. Regular prenatal check-ups and communication with your healthcare team are essential for a healthy pregnancy.

Sports Performance and Gluten-free/Vegan Diets
The impact of gluten-free and vegan diets on sports performance is a topic of interest for athletes and active individuals.
Effects on athletic performance depend on various factors such as individual needs, training demands, and overall nutrition. While some athletes may thrive on a gluten-free or vegan diet, others may require different nutritional strategies. It is important to understand that what works for one person may not work for another, and individualized approach is key.
Meeting increased nutritional demands is crucial in sports performance, regardless of dietary restrictions. Proper fueling before, during, and after exercise is important to support optimal performance and recovery. Athletes following a gluten-free diet may need to carefully choose gluten-free carbohydrates for energy. Vegan athletes must pay close attention to obtaining sufficient protein, iron, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids from plant-based sources.
Key nutrients for athletes include carbohydrates, protein, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and hydration. Balanced meal planning, along with appropriate timing and composition of meals, can ensure athletes have the necessary fuel for performance and recovery. For gluten-free athletes, focus on gluten-free grains, lean protein sources, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Vegan athletes should prioritize plant-based proteins, iron-rich foods, calcium-rich foods, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Recovery and muscle repair are essential aspects of sports performance. Adequate intake of protein and carbohydrates after exercise can help replenish glycogen stores and promote muscle repair. Vegan athletes can obtain protein from plant-based sources such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, and plant-based protein powders. Gluten-free athletes may choose gluten-free sources of protein such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and gluten-free grains.
Considerations for endurance vs. strength training should be taken into account when following a gluten-free or vegan diet. Endurance athletes may require higher carbohydrate intake to fuel prolonged exercise, while strength athletes may require higher protein intake to support muscle growth and recovery. Individual needs, goals, and training intensity should be evaluated when tailoring a diet to specific sports.
Mental Health and Gluten-free/Vegan Diets
The impact of diet on mental health has gained attention in recent years. Both gluten-free and vegan diets have the potential to influence mood and cognition.
Potential impact on mood and cognition is an area of interest when it comes to gluten-free and vegan diets. Gluten sensitivity or celiac disease can lead to neurological symptoms such as brain fog, anxiety, and depression. By eliminating gluten from your diet, you may experience improved mental clarity, better mood, and enhanced cognitive function.
Research on psychological well-being has shown that a vegan diet may have positive effects on mood and mental health. Plant-based diets tend to be rich in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats, which can support brain health and reduce inflammation. Additionally, the ethical and environmental considerations associated with a vegan diet can contribute to a sense of purpose and well-being.
The interplay of diet, gut health, and brain is an emerging field of research. The gut-brain axis refers to the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain. It is believed that the gut microbiome, which is influenced by diet, plays a significant role in mental health. Both gluten-free and vegan diets have the potential to positively impact the gut microbiome, which in turn may influence mental well-being.
Considerations for mental health conditions should be taken into account when following a gluten-free or vegan diet. Some individuals with mental health conditions may benefit from eliminating gluten or adopting a vegan diet, while others may not. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or mental health provider to determine the most appropriate dietary approach for your specific condition.
Role of nutrient deficiencies should also be considered when it comes to mental health and diet. Certain nutrient deficiencies, such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, have been linked to mental health disorders. It is important to ensure a well-rounded and balanced diet, along with appropriate supplementation if necessary, to support brain health and overall mental well-being.
In conclusion, both gluten-free and vegan diets offer a range of benefits for various aspects of health. From relief of digestive issues to improved heart health, weight management, and potential benefits for mental health, these diets can support overall well-being. It is important to approach these diets with knowledge, balance, and individualized considerations to ensure nutritional adequacy and long-term success. Seeking professional guidance and staying informed about potential challenges and pitfalls can help you make informed decisions and reap the benefits of these dietary approaches. Remember, making changes to your diet should be done with careful consideration and in consultation with healthcare professionals.
