If you suffer from joint pain or arthritis, finding the motivation to exercise might be challenging. However, staying active is crucial for managing your condition and improving your overall well-being. In this article, we will explore various ways that you can exercise safely and effectively, despite the discomfort caused by joint pain or arthritis. By incorporating these tips into your routine, you can maintain a healthy lifestyle and regain control of your physical health.
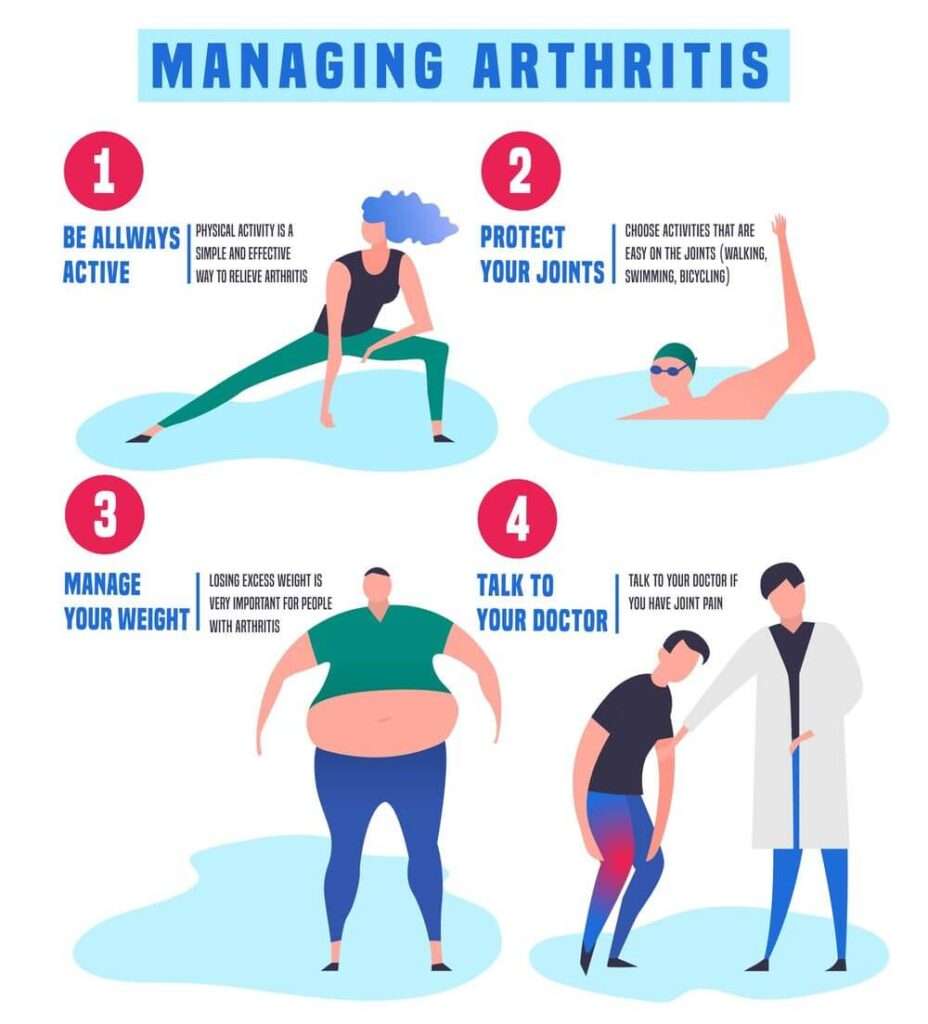
Understanding Joint Pain and Arthritis
What is joint pain?
Joint pain refers to discomfort, aches, or soreness in any of the body’s joints. The pain can vary in intensity, from mild to severe, and can affect one or multiple joints. Common areas of joint pain include the knees, hips, ankles, shoulders, and wrists. Joint pain can make everyday tasks challenging and can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a condition characterized by the inflammation and swelling of one or more joints. There are various types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. Osteoarthritis is the most common form and occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the joints wears down over time. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the joints.
Common causes of joint pain and arthritis
Joint pain and arthritis can have multiple causes, including age-related wear and tear, injuries, repetitive motions, genetic factors, and certain medical conditions. Obesity is also a major risk factor for developing joint pain and arthritis, as the excess weight puts additional stress on the joints. Understanding the underlying causes of joint pain can help in finding effective treatment and management strategies.
Impact of joint pain and arthritis on exercise
Joint pain and arthritis often make exercise challenging for individuals. The pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion can discourage physical activity, leading to decreased fitness levels. However, it is crucial to maintain an active lifestyle to manage joint pain and arthritis effectively. Exercise plays a crucial role in reducing pain, improving joint function, and promoting overall physical and mental well-being.
Benefits of Exercise for Joint Pain and Arthritis
Reducing pain and stiffness
Regular exercise helps to reduce joint pain and stiffness. Engaging in physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving chemicals in the brain. It also enhances blood circulation, which helps to flush out inflammatory substances and promote healing. Additionally, exercise releases synovial fluid, which lubricates the joints and reduces friction, resulting in less pain and stiffness.
Improving joint flexibility and range of motion
Exercise is essential for maintaining and improving joint flexibility and range of motion. When you engage in exercises that target the joints, such as stretching and range-of-motion exercises, it helps to keep the joints mobile. This can prevent joint stiffness, increase your ability to perform daily activities, and enhance your overall quality of life.
Strengthening muscles around the joints
Regular exercise helps to strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints. Strong muscles provide support and stability to the joints, reducing the stress and strain on them. By strengthening the muscles, you can alleviate some of the pressure on the joints, which can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
Promoting overall physical and mental well-being
Exercise is not only beneficial for joint pain and arthritis but also for your overall physical and mental well-being. Engaging in regular physical activity can help you maintain a healthy weight, reduce the risk of other chronic conditions, improve cardiovascular health, boost mood, and enhance cognitive function. It can also provide opportunities for social interaction and a sense of accomplishment, which can greatly improve your overall quality of life.
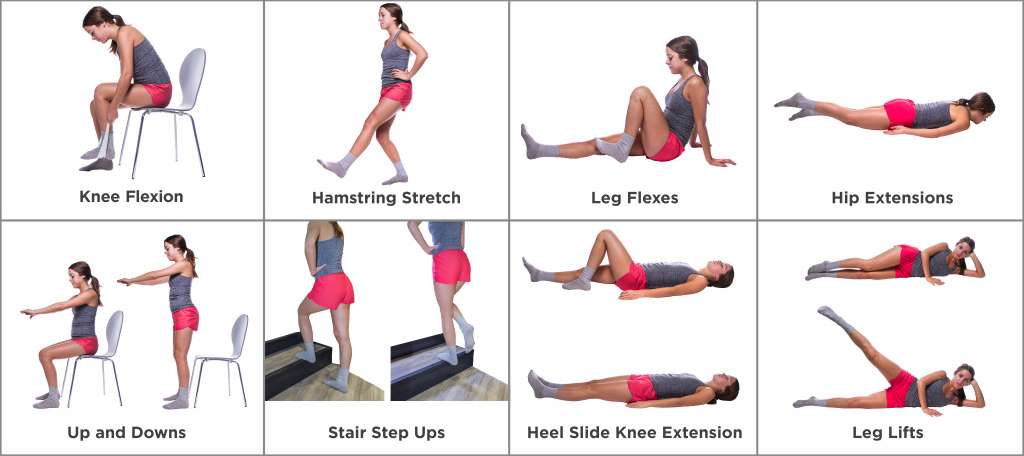
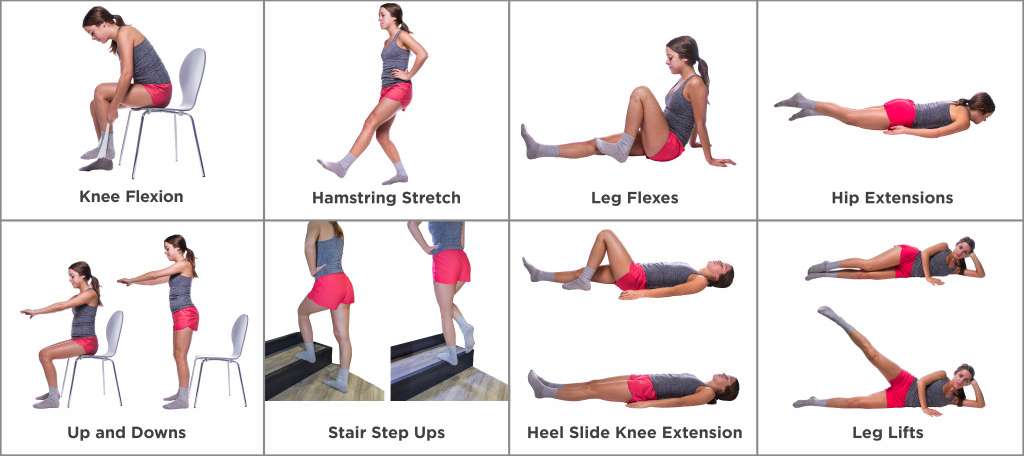
Types of Exercise Suitable for Joint Pain and Arthritis
Low-impact aerobic exercises
Low-impact aerobic exercises are gentle on the joints while still providing cardiovascular benefits. These exercises, such as walking, swimming, biking, and using an elliptical machine, can improve your endurance, strengthen your heart, and burn calories without putting excessive stress on the joints. Low-impact aerobic exercises are an excellent starting point for individuals with joint pain or arthritis.
Water exercises
Water exercises, also known as aquatic therapy or hydrotherapy, are highly beneficial for individuals with joint pain and arthritis. The buoyancy of water reduces the impact on the joints, making it easier to move and exercise. Water exercises, such as swimming, water aerobics, and water walking, can improve joint mobility, increase muscle strength, and alleviate pain and stiffness.
Strength training exercises
Strength training exercises help build muscle strength and improve joint stability. These exercises can be performed using resistance bands, free weights, weight machines, or bodyweight exercises. It is essential to start with low weights and gradually increase resistance to avoid putting excessive stress on the joints. Strengthening the muscles around the joints can help alleviate joint pain and improve overall joint function.
Range-of-motion exercises
Range-of-motion exercises are designed to increase joint flexibility and maintain or improve the full range of motion in the joints. These exercises involve moving a joint as far as possible in different directions without causing pain. Examples of range-of-motion exercises include shoulder rolls, wrist circles, ankle alphabet, and neck rotations. Regular practice of range-of-motion exercises can prevent stiffness, maintain joint function, and reduce the risk of developing contractures.
Tai Chi and Yoga
Tai Chi and yoga are mind-body exercises that can be particularly beneficial for individuals with joint pain and arthritis. These exercises focus on gentle movements, stretching, deep breathing, and meditation. Tai Chi and yoga improve balance, flexibility, joint strength, and mental well-being. They can also help manage stress, which is essential for individuals with chronic pain conditions.
Warm-up and Cool-down Techniques
Importance of warm-up and cool-down
Prior to any exercise session, it is important to warm up the body to prepare the muscles and joints for activity. Warm-up exercises increase blood flow to the muscles, raise body temperature, and help to prevent injuries. Similarly, a cool-down routine is essential to gradually bring down the heart rate, prevent dizziness, and flush out metabolic waste products. Warm-up and cool-down techniques should be an integral part of your exercise routine, especially if you have joint pain or arthritis.
Dynamic stretching exercises for warm-up
During the warm-up phase, dynamic stretching exercises are recommended. Dynamic stretching involves moving parts of your body through a full range of motion in a controlled manner. This helps to increase blood flow, warm up the muscles, and improve joint mobility. Examples of dynamic stretching exercises include leg swings, arm circles, walking lunges, and torso rotations.
Gentle static stretches for cool-down
During the cool-down phase, gentle static stretches are recommended. Static stretches involve holding a specific position without moving. This helps to prevent muscle tightness, improve flexibility, and promote relaxation. It is important to hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds without bouncing or causing pain. Examples of gentle static stretches include calf stretches, hamstring stretches, shoulder stretches, and neck stretches.

Tips for Exercising with Joint Pain or Arthritis
Consultation with a healthcare professional
Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or physical therapist, is essential before starting any exercise program, especially if you have joint pain or arthritis. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific condition and help create an exercise plan that is safe and effective for you.
Start slowly and gradually increase intensity
When starting an exercise program, it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity. This allows your body to adapt to the new demands and reduces the risk of injury. Begin with shorter durations and lower intensities, and slowly progress over time. Listen to your body and only push yourself as far as feels comfortable.
Listen to your body’s signals
Pay attention to your body’s signals during exercise. If you experience pain, discomfort, or swelling, it is important to modify or stop the activity. Pushing through pain can worsen the condition and lead to further injury. Always prioritize your comfort and well-being during exercise.
Use proper form and technique
Using proper form and technique during exercise is crucial to prevent injury and maximize the benefits. If you are unsure about the correct form, consider working with a certified fitness professional or physical therapist who can guide you. They can teach you proper body mechanics and ensure that you are performing exercises correctly and safely.
Choose the right equipment and footwear
Choosing the right equipment and footwear is important to support your joints and minimize the risk of injury. Invest in shoes that provide adequate cushioning, stability, and support. Consider using joint supports, such as braces or wraps, if recommended by your healthcare professional.
Manage pain and inflammation
If you experience pain or inflammation after exercise, it is important to manage it effectively. Use ice packs or cold compresses to reduce swelling and relieve pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be recommended by your healthcare professional to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Alternate exercise activities
To prevent overuse injuries and maintain a balanced exercise routine, it is beneficial to alternate between different types of exercises. This can help reduce repetitive stress on specific joints and muscles, while still providing a variety of benefits. Mixing low-impact aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises can ensure that all aspects of your fitness are addressed.
Monitor and track your progress
Monitoring and tracking your progress can help you stay motivated and know when to make adjustments to your exercise routine. Keep a record of your workouts, noting the duration, intensity, and any modifications or improvements. This will allow you to see your progress over time and make informed decisions about your exercise program.
Exercises to Avoid or Modify
High-impact activities
High-impact activities, such as running, jumping, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), can put excessive stress on the joints and exacerbate joint pain or arthritis. It is advisable to avoid or modify these activities to prevent further damage. Instead, opt for low-impact exercises that provide cardiovascular benefits without the joint impact.
Exercises that put excessive stress on joints
Certain exercises, such as heavy weightlifting or repetitive movements, can put excessive stress on the joints and potentially worsen joint pain or arthritis. It is important to choose exercises that are gentle on the joints and do not exacerbate your symptoms. If you are unsure about a particular exercise, consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.
Activities with repetitive motions
Activities with repetitive motions, such as running on a treadmill or cycling long distances, can cause overuse injuries and exacerbate joint pain or arthritis. It is advisable to incorporate variety into your exercise routine and avoid excessive repetition. This will prevent excessive stress on specific joints and allow for proper recovery.
Exercises involving twisting or jerking motions
Exercises that involve twisting or jerking motions, such as certain types of weightlifting or contact sports, can increase the risk of joint injury and aggravate joint pain or arthritis. It is important to choose exercises that promote controlled, smooth movements without sudden or forceful actions. Always prioritize the safety and well-being of your joints.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Medical clearance and supervision
Before starting any exercise program, it is important to obtain medical clearance from your healthcare professional, especially if you have joint pain or arthritis. They can assess your condition, provide specific recommendations, and monitor your progress. If you have any limitations or concerns, consider working with a qualified exercise specialist, physical therapist, or trainer who can provide guidance and support.
Use of assistive devices if necessary
If you have difficulty with mobility or stability, the use of assistive devices can be beneficial during exercise. This may include using walking aids, braces, or adaptive equipment. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine if and when assistive devices are necessary for your specific needs.
Appropriate warm-up and cool-down
As mentioned earlier, warm-up and cool-down exercises are crucial to prevent injuries and maintain joint health. Ensure that you dedicate sufficient time to both warm-up and cool-down activities in your exercise routine. This will help prepare your body for physical activity and promote optimal recovery.
Avoiding overexertion and pushing through pain
It is important to listen to your body and avoid overexertion during exercise. Pushing through pain or fatigue can worsen joint pain or arthritis and lead to further injury. Pace yourself, take breaks as needed, and gradually increase the intensity or duration of your workouts over time.
Monitoring and managing inflammation
Inflammation is common in individuals with joint pain or arthritis. It is important to monitor and manage inflammation effectively to prevent worsening of symptoms. If you experience increased swelling, redness, or warmth in the joints, consult with your healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options.
Knowing when to rest and recover
Rest and recovery are as important as exercise itself. Pay attention to your body’s signals and allow yourself ample time to rest and recover between exercise sessions. This will help prevent overuse injuries, reduce the risk of joint pain flare-ups, and optimize your overall exercise performance and results.
Maintaining a Balanced Exercise Routine
Incorporating variety into workouts
To maintain a balanced exercise routine, it is important to incorporate variety into your workouts. This can prevent boredom, engage different muscle groups, and ensure that all aspects of your fitness are addressed. Include a combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises in your weekly routine.
Balancing cardiovascular, strength, and flexibility exercises
A well-rounded exercise routine should include cardiovascular, strength, and flexibility exercises. Cardiovascular exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, improve heart health and endurance. Strength training exercises build muscle strength and protect the joints. Flexibility exercises, such as stretching or yoga, enhance joint mobility and prevent stiffness. Balancing these different types of exercises will help you maintain overall fitness and joint health.
Giving rest days to allow recovery
Rest days are essential for allowing your body to recover and repair itself. Incorporate rest days into your exercise routine to prevent overuse injuries and burnout. This will also give your joints time to rest and reduce any joint pain or inflammation that may occur from frequent exercise.
Considering cross-training or alternative exercises
Cross-training involves participating in a variety of activities to challenge different muscle groups and reduce the risk of overuse injuries. Consider incorporating cross-training or alternative exercises into your routine, such as swimming instead of running or yoga instead of weightlifting. This can provide a refreshing change of pace and prevent excessive stress on specific joints.
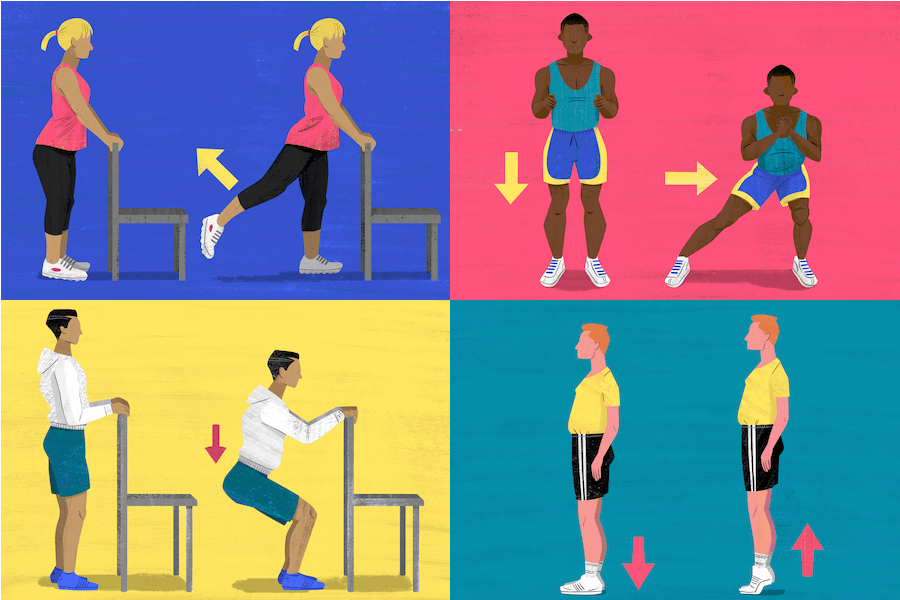
Additional Tips for Managing Joint Pain
Maintaining a healthy weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing joint pain and arthritis. Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, leading to increased pain and inflammation. Follow a balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, to support a healthy weight and reduce the burden on your joints.
Eating a nutritious and anti-inflammatory diet
In addition to maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a nutritious and anti-inflammatory diet can improve joint health. Include foods that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties, such as fatty fish, nuts, seeds, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Consult with a registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific needs.
Applying heat or cold therapy
Heat and cold therapy can provide temporary relief from joint pain and inflammation. Applying a heating pad or warm towel to the affected area can help relax muscles, improve blood flow, and reduce stiffness. Conversely, applying a cold pack or ice wrapped in a cloth can numb the area and help reduce pain and inflammation. Consult with your healthcare professional to determine which therapy is most appropriate for your specific condition.
Using topical creams or ointments
Topical creams or ointments containing ingredients like menthol, camphor, or capsaicin can provide temporary relief from joint pain. These products work by numbing the area or creating a warming or cooling sensation. Look for over-the-counter options or consult with your healthcare professional for suitable topical treatments.
Considering supplements or natural remedies
Certain supplements, such as glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids, may offer benefits for joint health. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare professional before starting any supplements, as they can interact with medications or have side effects. Additionally, some individuals find relief from natural remedies, such as turmeric or ginger, but their effectiveness varies from person to person.
Engaging in stress-reducing activities
Chronic pain, including joint pain, can be exacerbated by stress. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies, can help manage pain and promote overall well-being. Find activities that help you relax and unwind, and make them a regular part of your routine.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can be immensely helpful for individuals with joint pain or arthritis. A physical therapist can assess your specific condition, create a personalized exercise program, and provide hands-on treatments to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and increase functionality. They can guide you through proper exercise techniques and recommend assistive devices or modifications as needed.
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on helping individuals with joint pain or arthritis adapt their daily activities to maximize function and minimize pain. An occupational therapist can provide strategies to conserve energy, suggest assistive devices or modifications for daily tasks, and guide you in exercises to improve joint mobility and strength.
Exercise specialists
Exercise specialists, such as certified personal trainers or exercise physiologists, have specific knowledge and expertise in designing exercise programs for individuals with joint pain or arthritis. They can create a tailored exercise routine, teach proper form and technique, monitor your progress, and make necessary adjustments to your program.
Arthritis support groups
Joining arthritis support groups can provide valuable emotional support and practical tips for managing joint pain and arthritis. These groups offer a platform to connect with others who are facing similar challenges, share experiences, and learn from one another. Support groups can provide a sense of community and motivation to stay active and positive despite the challenges of arthritis.
In conclusion, exercising with joint pain or arthritis is not only possible but also highly beneficial. By understanding joint pain and arthritis, recognizing the benefits of exercise, knowing the types of suitable exercises, and following safety precautions, you can effectively manage joint pain, improve joint function, and enhance your overall well-being. Seek professional guidance when needed, listen to your body, and make exercise a regular part of your life to maintain a healthy and active lifestyle.