Are you curious about how to calculate your ideal macronutrient ratio? Well, look no further! In this article, we will guide you through the process of determining the perfect balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to optimize your health and fitness goals. Whether you’re aiming to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, understanding your macronutrient needs is crucial. So, let’s get started on your journey to finding the ideal macronutrient ratio that suits you best.
Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the three primary nutrients that our bodies require in large quantities for energy and overall functioning: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Understanding the role of macronutrients is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet and achieving optimal nutrition.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are found in foods such as grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is utilized by our cells for energy. They also provide essential dietary fiber and can impact blood sugar levels. It is important to choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and legumes, which offer more sustained energy and nutrients compared to simple carbohydrates like refined sugars.
Proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of the body and are vital for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. They are found in foods such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and plant-based sources like tofu and quinoa. Proteins are composed of amino acids that play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including enzyme production, immune function, and hormone regulation. It is important to consume a variety of protein sources to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
Fats
Fats are essential for proper bodily function, as they provide energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and help absorb certain vitamins. Examples of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon. It is necessary to include healthy fats in our diet while being mindful of portion sizes, as fats are higher in calories than carbohydrates and proteins.
Importance of Macronutrient Ratio
Understanding the macronutrient ratio that best suits your dietary needs is crucial for several reasons.
Weight Management
The macronutrient ratio you consume can impact weight management. Different macronutrient combinations can help control appetite, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote the feeling of fullness. For example, a higher protein intake may help you feel satiated for longer periods and reduce overall caloric intake, which can aid in weight loss.
Energy Levels
The right macronutrient ratio can impact your energy levels throughout the day. Carbohydrates provide quick energy, while fats offer sustained energy and proteins help with muscle recovery. Balancing the intake of these macronutrients can help maintain stable energy levels and prevent energy crashes.
Muscle Gain or Preservation
Proteins play a critical role in muscle repair and growth. If your goal is to build or maintain muscle mass, ensuring an adequate protein intake is essential. Additionally, consuming carbohydrates before and after intense workouts can provide the energy necessary for muscle development and recovery. Fats also play a role in supporting muscle health and overall body composition.
Health Considerations
Different macronutrient ratios can impact various health conditions. For example, individuals with diabetes may need to focus on controlling carbohydrate intake to manage blood sugar levels. Those with heart disease may benefit from a diet low in saturated fats, while individuals with certain metabolic disorders may require specific macronutrient ratios tailored to their condition.

Determining Your Macronutrient Ratio
Determining your ideal macronutrient ratio requires a personalized approach based on your individual needs and goals. Here are the steps to determine your macronutrient ratio:
Step 1: Set Your Calorie Intake
To begin, it is essential to determine your daily calorie intake. This can be done by assessing factors such as age, gender, weight, height, activity level, and goal (weight loss, maintenance, or gain). Various online calculators and apps can help estimate your calorie needs.
Step 2: Calculate Your Protein Needs
Protein needs are generally calculated based on a percentage of your total calorie intake. The general recommendation is to consume around 10-35% of your daily calories from protein sources. Multiply your total calorie intake by the desired percentage to determine the number of calories from protein. Then, divide this number by 4 (as there are 4 calories per gram of protein) to determine the grams of protein needed.
Step 3: Determine Your Fat Intake
Similarly, fat intake can be calculated as a percentage of your total calorie intake. The recommended range for fat intake is generally 20-35% of your daily calories. Multiply your total calorie intake by the preferred percentage and divide that number by 9 (as there are 9 calories per gram of fat) to determine the grams of fat needed.
Step 4: Calculate Your Carbohydrate Needs
Once the protein and fat intake is determined, the remaining calories in your desired macronutrient ratio can be allocated to carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide 4 calories per gram, so divide the remaining calories by 4 to determine the grams of carbohydrates needed.
Factors Influencing Macronutrient Ratio
Several factors influence the ideal macronutrient ratio for an individual. Understanding these factors can help personalize your dietary approach.
Activity Level
Your level of physical activity plays a significant role in determining your macronutrient ratio. Those with higher activity levels, such as athletes or individuals engaging in intense exercise, may require higher carbohydrate and protein intake. Conversely, individuals with a sedentary lifestyle may benefit from a lower carbohydrate intake.
Body Composition Goals
Whether your goal is weight loss, muscle gain, or weight maintenance, your macronutrient ratio should be adjusted accordingly. For example, a higher protein intake may be beneficial for muscle gain, while a lower carbohydrate intake may aid in weight loss. Consultation with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can help tailor your macronutrient ratio to your specific goals.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain health conditions may require specific macronutrient ratios. For instance, individuals with diabetes may benefit from a diet lower in carbohydrates to manage blood sugar levels. Similarly, those with conditions like kidney disease or certain metabolic disorders may need to modify their macronutrient intake to support their overall health.
Personal Preferences
Personal preferences and dietary restrictions should also be considered when determining your macronutrient ratio. If you follow a specific diet, such as vegetarian or vegan, modifications may need to be made to ensure you meet your nutritional needs while adhering to your dietary choices. Consulting a healthcare professional can help address any concerns and provide guidance.
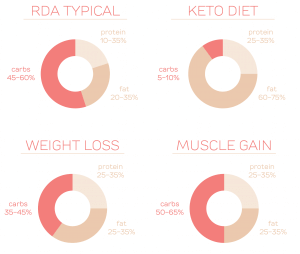
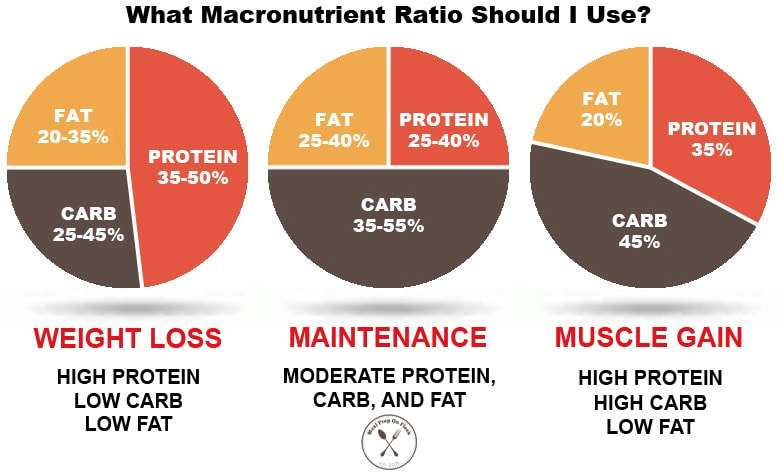
Recommended Macronutrient Ratios
There are several macronutrient ratios that have gained popularity for their potential benefits. Here are some common examples:
The American Diet
The typical American diet is often high in carbohydrates, consisting of about 45-65% of total calories from carbohydrates, 20-35% from fats, and 10-35% from protein. This ratio is based on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and can serve as a general guideline for individuals with no specific dietary needs or goals.
Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that is commonly used for weight loss and managing certain health conditions. This diet typically involves consuming 5-10% of total calories from carbohydrates, 70-80% from fats, and 10-20% from protein. It aims to shift the body into a state of ketosis, where it utilizes fats for energy instead of carbohydrates.
Zone Diet
The Zone diet focuses on a balanced macronutrient ratio to control inflammation and stabilize blood sugar levels. The recommended ratio is approximately 40% carbohydrates, 30% fats, and 30% protein. This diet emphasizes consuming low glycemic index carbohydrates, healthy fats, and lean protein sources.
Low-Fat Diet
Low-fat diets are often recommended for individuals aiming to reduce their total fat intake and manage weight or heart health. These diets typically involve consuming 60-70% of total calories from carbohydrates, 10-20% from fats, and 10-20% from protein. It is important to choose sources of healthy fats and monitor overall calorie intake.
Balanced Macronutrient Ratio
A balanced macronutrient ratio is designed to provide an equal distribution of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. This ratio generally consists of approximately 33% of total calories from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It promotes a balanced diet that supports overall health and well-being.
Tools for Calculating Macronutrient Ratio
There are several tools available to help calculate and track your macronutrient ratio. These tools can provide a starting point, but it is essential to consider individual needs and goals.
Online Macronutrient Calculators
Online macronutrient calculators are widely available and can estimate your macronutrient needs based on your personal information, activity level, and goals. These calculators provide a general guideline, but consulting with a registered dietitian can offer personalized advice.
Mobile Apps
Mobile apps can track your daily food intake and calculate macronutrient ratios. They often have large databases of food items and can provide a breakdown of your daily intake. Some apps also offer features like goal setting, meal planning, and recipe suggestions.
Registered Dietitians
Registered dietitians are nutrition professionals who can assess your specific needs and provide personalized advice based on your goals, preferences, and health conditions. They can perform a comprehensive evaluation and create a personalized macronutrient ratio that suits your individual needs.
Adjusting Macronutrient Ratio
Once you have determined your initial macronutrient ratio, it is important to monitor and make adjustments as needed.
Monitoring and Adjusting
Regularly monitoring your progress and assessing how you feel is crucial. Keep track of your energy levels, appetite, and mood to determine if any adjustments need to be made. It is essential to remember that macronutrient ratios can be individualized, and what works for one person may not work for another.
Optimal Macronutrient Ratios for Specific Goals
Specific goals, such as weight loss, muscle gain, or managing certain health conditions, may require specific macronutrient adjustments. Working with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help determine the optimal macronutrient ratio for your individual needs.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
While determining your macronutrient ratio, certain challenges may arise. Here are some potential challenges and solutions:
Food Allergies or Intolerances
Individuals with food allergies or intolerances may face challenges in meeting their macronutrient needs. It is important to find suitable alternatives and substitutions that fit within your dietary restrictions. Consulting with a dietitian can provide guidance on suitable options and ensure nutritional needs are met.
Vegetarian or Vegan Diets
Vegetarian or vegan diets may require additional considerations to ensure all essential nutrients are obtained. Special attention should be given to protein sources, iron, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids. Including a variety of plant-based protein sources, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and fortified foods can help meet macronutrient needs.
Budget Constraints
For individuals on a limited budget, meeting macronutrient needs may pose a challenge. It is essential to prioritize nutrient-dense foods that provide the greatest nutritional value for the cost. Options such as bulk purchases, seasonal produce, and plant-based protein sources can be cost-effective choices.

Monitoring Progress and Making Changes
Regularly monitoring your progress and assessing the effectiveness of your macronutrient ratio is important for long-term success. Here are some ways to monitor progress and make changes as needed:
Regular Assessments
Regularly assess your energy levels, weight, body composition, and overall sense of well-being. Monitoring these factors can help determine if any adjustments to your macronutrient ratio are necessary.
Work with a Healthcare Professional
Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide additional guidance and support. They can assess your progress, help make necessary adjustments, and address any questions or concerns you may have.
Conclusion
Understanding your macronutrient ratio is an essential aspect of achieving a balanced and nutritious diet. By considering factors such as your goals, activity level, and personal preferences, you can determine the macronutrient ratio that suits your individual needs. Remember to monitor how your body responds to different ratios and make adjustments as needed. Working with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance to help you optimize your macronutrient intake for overall health and well-being.