You’re on a quest for a healthier lifestyle, and the world of diets is calling your name. But with so many options out there, how can you navigate through the sea of information and find the best approach for you? Fear not, because today we’re diving into the differences between low-carb and keto diets, giving you the insights you need to make an informed decision.
In the realm of nutrition, these two diets have been making waves, promising weight loss, increased energy, and improved overall health. But what sets them apart? While both low-carb and keto diets limit your carbohydrate intake, they differ in their approach and desired outcomes. So, grab a cup of tea, kick back, and let’s explore the ins and outs of these popular diets, empowering you to make the right choice for your unique wellness journey.
Definition of Low-carb and Keto Diets
Low-carb Diet
a low-carb diet is a dietary approach that focuses on reducing the intake of carbohydrates, primarily found in foods such as grains, legumes, fruits, and starchy vegetables. This diet promotes the consumption of foods that are higher in protein and fat, while restricting the amount of carbohydrates consumed. The goal of a low-carb diet is to shift the body’s primary source of fuel from carbohydrates to fats, leading to potential weight loss and improved overall health.
Keto Diet
A keto diet, short for ketogenic diet, is a more specific variation of a low-carb diet. It involves drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat intake to encourage the body to enter a state of ketosis. Ketosis is a metabolic state where the body primarily relies on fat for fuel instead of glucose derived from carbohydrates. This dietary approach aims to achieve a state of ketosis by restricting carbohydrate intake to a very low level, typically below 50 grams per day, and increasing fat intake significantly.
Macronutrient Composition
Low-carb Diet
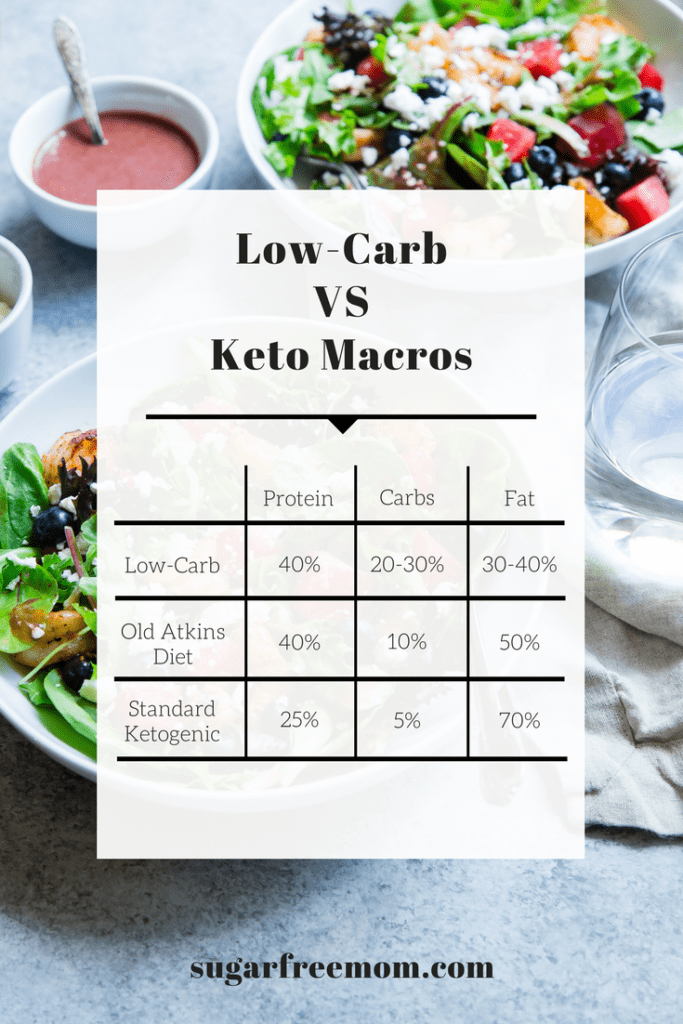
In a low-carb diet, the macronutrient composition may vary depending on individual preferences and specific diet plans. However, the general guidelines for a low-carb diet typically involve consuming around 20-40% of calories from carbohydrates, 30-40% from protein, and 30-40% from fats. The emphasis is on reducing carbohydrate intake while maintaining a moderate intake of protein and fat.
Keto Diet
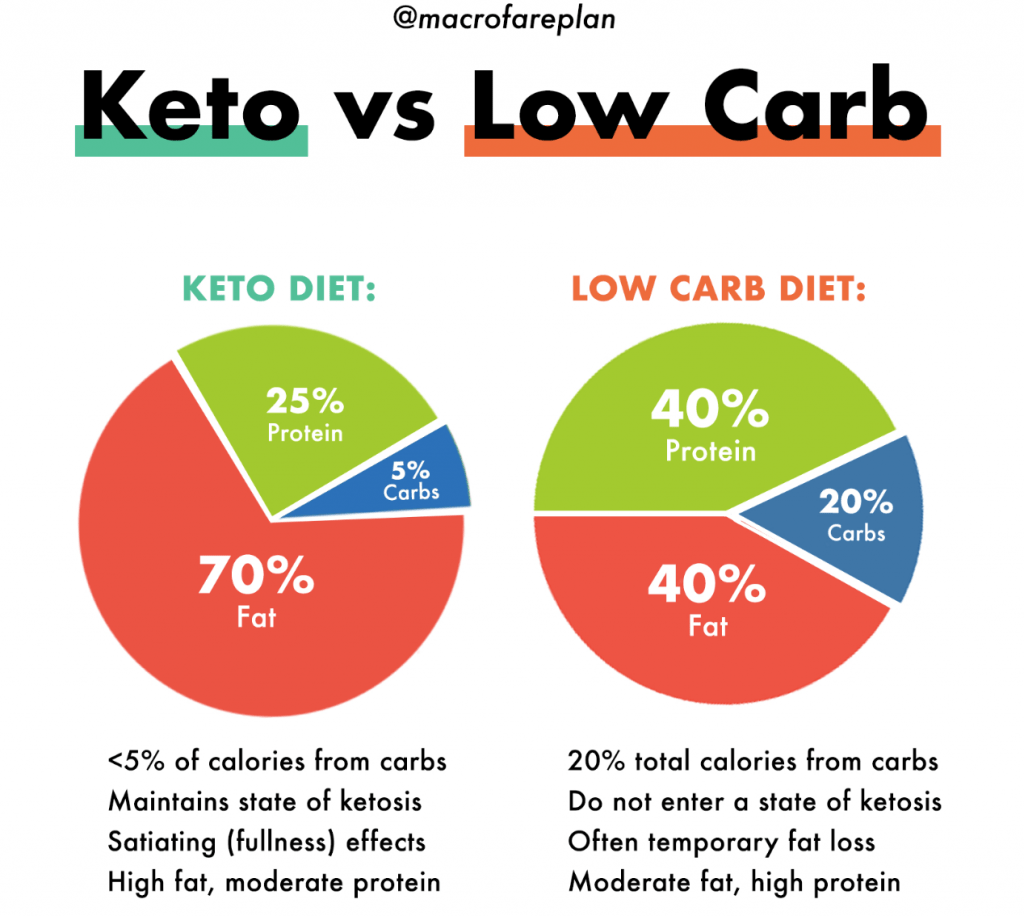
A keto diet has a distinct macronutrient composition compared to a low-carb diet. The primary focus is on consuming very low amounts of carbohydrates, typically around 5-10% of total calorie intake. The majority of calories, around 70-75%, come from healthy fats, while the remaining 20-25% comes from protein. This macronutrient ratio is designed to induce ketosis and shift the body’s metabolism to primarily rely on fat for energy.

Purpose and Benefits
Low-carb Diet
The purpose of a low-carb diet is to reduce carbohydrate intake, which can lead to various benefits. A low-carb diet can help promote weight loss by stabilizing blood sugar levels, reducing the production of insulin, and controlling hunger hormones. It may also improve heart health by lowering triglyceride levels and increasing levels of “good” HDL cholesterol. Additionally, a low-carb diet may help regulate blood pressure, improve mental clarity, and enhance overall energy levels.
Keto Diet
The main purpose of a keto diet is to induce a state of ketosis. This metabolic state offers several potential benefits, including significant weight loss, enhanced mental focus, and increased energy levels. Ketosis can also improve insulin sensitivity and help individuals with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. Additionally, the keto diet has been studied for its potential therapeutic benefits in managing epilepsy, reducing inflammation, and improving neurological conditions.
Carbohydrate Limit
Low-carb Diet
In a low-carb diet, the carbohydrate limit may vary depending on specific dietary plans and individual needs. However, the general recommendation is to consume around 50-150 grams of carbohydrates per day for most people. This allows for a moderate intake of carbohydrates while still promoting the benefits of a low-carb approach.
Keto Diet
The carbohydrate limit in a keto diet is significantly lower than that of a low-carb diet. To achieve and maintain a state of ketosis, individuals typically restrict their carbohydrate intake to around 20-50 grams per day. This strict limitation is necessary to deplete the body’s glycogen stores and switch to using ketones as the primary source of energy.
Protein Intake
Low-carb Diet
Protein intake is generally moderate in a low-carb diet, with recommendations typically ranging from 15-30% of total calorie intake. This allows for an adequate protein intake to support muscle growth, repair, and overall health. Protein-rich foods like lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, and plant-based sources are typically included in a low-carb diet.
Keto Diet
Protein intake is also moderate in a keto diet, with recommendations usually falling between 20-25% of total calorie intake. Consuming an appropriate amount of protein is important to prevent muscle loss and support various bodily functions. Foods high in protein, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products, are commonly included in a keto diet.
Fat Intake
Low-carb Diet
Fat intake in a low-carb diet can vary depending on personal preferences and chosen dietary plan. However, it generally focuses on including healthy sources of fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish. The goal is to increase fat consumption to replace some of the calories usually obtained from carbohydrates.
Keto Diet
Fat intake is significantly increased in a keto diet, typically comprising around 70-75% of total calorie intake. This high-fat approach encourages the body to utilize fats as the primary source of fuel. Foods rich in healthy fats, including avocados, nuts, seeds, coconut oil, and butter, are staples in a keto diet.

Ketosis
Low-carb Diet
While a low-carb diet can promote weight loss and other health benefits, it does not necessarily guarantee a state of ketosis. The moderate reduction in carbohydrate intake may result in somewhat lower blood sugar and insulin levels, but it may not be sufficient to fully enter ketosis. However, some individuals may naturally reach a mild state of ketosis on a low-carb diet, especially if they are physically active.
Keto Diet
The key objective of a keto diet is to achieve and maintain a state of ketosis. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the body shifts its metabolic state and begins producing ketones. Ketones are molecules formed when the body breaks down fats for energy in the absence of sufficient glucose from carbohydrates. This metabolic state is known as ketosis and is the hallmark of a keto diet.
Food Choices
Low-carb Diet
On a low-carb diet, the emphasis is on reducing carbohydrate intake while incorporating a variety of nutritious foods. Some examples of commonly included food choices are lean meats, poultry, fish, non-starchy vegetables, low-sugar fruits, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats. Processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-carbohydrate foods should be limited or avoided.
Keto Diet
A keto diet involves specific food choices that are low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats. Foods rich in monounsaturated and saturated fats, such as avocados, coconut oil, nuts, and seeds, are often encouraged. Protein sources like meat, fish, and eggs are commonly consumed. Additionally, non-starchy vegetables, full-fat dairy products, and low-sugar fruits such as berries are typically included. High-carbohydrate foods, grains, legumes, and most fruits are significantly restricted or eliminated.
Health Effects
Low-carb Diet
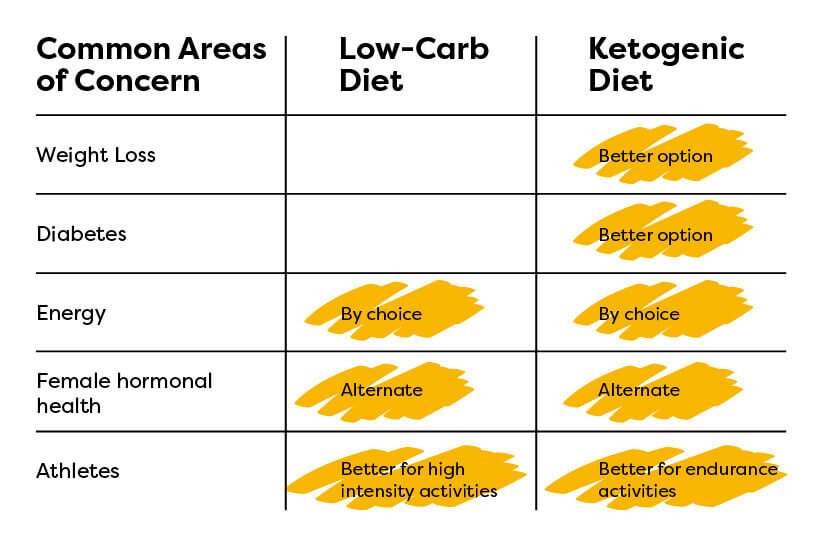
A low-carb diet can have various positive health effects. It may lead to weight loss, improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of heart disease, and increased levels of good cholesterol. Some individuals may also experience improved mental clarity and reduced inflammation. However, it is important to note that the long-term effects of a low-carb diet, especially in relation to cardiovascular health and nutrient deficiencies, require further research.
Keto Diet
The keto diet has been studied for its potential health effects, but further research is still needed. Some studies suggest that a keto diet may be an effective approach for weight loss, managing blood sugar levels, and improving certain neurological conditions. However, it is essential to note that a keto diet can have potential side effects in the short term, such as the “keto flu” and digestive issues. Individuals with certain medical conditions or taking certain medications should consult with a healthcare professional before starting a keto diet.
Sustainability
Low-carb Diet
A low-carb diet can be sustainable for many individuals, as it allows for flexibility in food choices and does not require strict macronutrient calculations or ketone monitoring. It can be adapted to various dietary preferences and lifestyles, making it easier to follow in the long term. However, it is important to maintain a balanced approach and ensure an adequate intake of essential nutrients from a wide range of whole foods.
Keto Diet
The sustainability of a keto diet can vary depending on individual preferences and health goals. While some individuals may find it relatively easy to maintain a keto lifestyle, others may find the strict carbohydrate restrictions challenging. Adhering to a ketogenic diet often involves careful meal preparation, tracking macronutrient intake, and monitoring ketone levels. It may require more planning and effort to sustain over time compared to a low-carb or more balanced approach.
In conclusion, both low-carb and keto diets have similarities and differences in their macronutrient composition, purpose, and health effects. A low-carb diet focuses on reducing carbohydrate intake while including moderate amounts of protein and fat. A keto diet, on the other hand, requires a very low carbohydrate intake, a higher percentage of fat, and a moderate protein intake to achieve and maintain ketosis. Both approaches can offer weight loss benefits, improved blood sugar control, and increased energy levels. Choosing the most suitable diet depends on individual preferences, health goals, and considerations. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new dietary approach to ensure it aligns with personal needs and overall health.
