If you’ve ever wondered about the crucial role that protein plays in building muscle, look no further. In this article, you’ll discover the fascinating relationship between protein and muscle growth. It’s time to unravel the mystery and uncover the science behind how protein fuels and supports the development of lean muscle mass. Get ready to gain a deeper understanding of the essential role protein plays in your fitness journey.
Protein and Muscle Building
If you’ve ever wondered about the role of protein in building muscle, you’re in the right place. Protein plays a vital role in muscle growth and development, acting as the building blocks for your muscles. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the essential components of protein, protein synthesis, the importance of protein quality, timing and frequency of protein consumption, protein supplementation, balancing protein intake with other nutrients, and potential risks associated with excessive protein consumption. So let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of protein and muscle building!
Protein as the Building Blocks
When it comes to building muscle, protein is the star of the show. Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the essential components responsible for muscle growth and repair. Each amino acid is like a brick, and when combined, they form proteins that serve as the building blocks for your muscles. So, it’s safe to say that without adequate protein intake, your muscle-building efforts may be compromised.

Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process by which your body builds new proteins, including muscle proteins. It involves the creation of new muscle tissue and the repair of damaged muscle fibers. During protein synthesis, your body takes the amino acids from the protein you consume and assembles them into new proteins, which are then used for muscle growth. This ongoing process of protein synthesis is crucial for maintaining and increasing muscle mass.
Protein Intake and Muscle Growth
Now that you understand the role of protein in muscle building and protein synthesis, it’s crucial to address the question of protein intake. How much protein do you actually need to support muscle growth? The answer may vary depending on factors such as your activity level, body composition goals, and individual differences.

Amino Acids: The Essential Components
To understand protein’s role in muscle building, it’s essential to delve into the world of amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and there are two main categories: essential and non-essential amino acids.
Essential vs. Non-Essential Amino Acids
Essential amino acids are those that your body cannot produce on its own, so you must obtain them through your diet. They include amino acids such as leucine, isoleucine, and valine, which are key players in muscle protein synthesis. On the other hand, non-essential amino acids can be produced by your body, so you don’t need to rely solely on dietary sources to meet your needs.
Branch Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
Branch chain amino acids (BCAAs) are a subset of essential amino acids that have gained significant attention in the world of muscle building. BCAAs, including leucine, isoleucine, and valine, have been shown to play a crucial role in promoting muscle protein synthesis. They are particularly beneficial when consumed during or after exercise, as they can help enhance muscle recovery and reduce exercise-induced muscle damage.
Leucine: The Key Amino Acid
Leucine, one of the essential amino acids, deserves special mention due to its significant role in muscle building. It’s considered the key amino acid when it comes to stimulating muscle protein synthesis. Studies have shown that consuming leucine-rich foods or supplements can enhance muscle protein synthesis and promote muscle growth. So, if you’re looking to optimize your muscle-building potential, be sure to include adequate amounts of leucine in your diet.
Protein Quality Matters
Not all proteins are created equal, and the quality of protein you consume can impact your muscle-building endeavors. So, what determines protein quality?
Protein Digestibility
Protein digestibility is a measure of how well your body can break down and absorb the amino acids from a specific protein source. High-quality proteins are easily digested and provide a rich source of essential amino acids for muscle building. On the other hand, proteins with low digestibility may not be as effective in promoting muscle growth. Therefore, opting for protein sources with high digestibility is crucial for optimizing muscle protein synthesis.
Complete Proteins
Complete proteins contain all the essential amino acids required by your body in appropriate amounts. Animal-based protein sources, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products, are considered complete proteins. These sources provide a wide range of amino acids, making them ideal for supporting muscle growth. However, if you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, don’t worry! You can still obtain complete proteins by combining different plant-based protein sources.
Sources of High-Quality Protein
Incorporating high-quality protein sources into your diet is essential for muscle growth. In addition to animal-based protein sources, there are also plant-based options that can provide the necessary amino acids for muscle building. Some examples of high-quality protein sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, and quinoa. By including a variety of these protein sources, you can ensure that your body receives the essential amino acids needed for muscle growth.
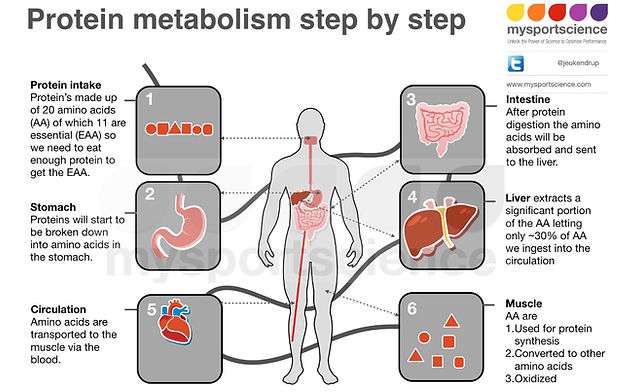
Timing and Frequency of Protein Consumption
Protein timing and frequency of consumption play a significant role in maximizing muscle protein synthesis and promoting muscle growth. Let’s explore the different aspects of protein timing to optimize your muscle-building potential.
Post-Workout Protein
Consuming protein after your workout is crucial for kick-starting the muscle recovery process. During exercise, your muscles undergo stress and microdamage, and providing them with the necessary amino acids post-workout helps repair and rebuild the damaged muscle fibers. Aim to consume a protein-rich snack or meal within the first hour after your workout to maximize the benefits of post-workout protein intake.
Pre-Workout Protein
While post-workout protein is important for recovery, don’t overlook the benefits of pre-workout protein consumption. Consuming protein before your workout can help provide the necessary amino acids your muscles require during the exercise session. It can also help prevent muscle breakdown and promote muscle protein synthesis. Choose easily digestible protein sources, such as a protein shake or a small meal containing lean protein and carbohydrates, to fuel your exercise session.
Protein throughout the Day
In addition to post-workout and pre-workout protein intake, spreading your protein consumption throughout the day is also important. Aim to include protein in every meal and snack to provide your muscles with a constant supply of amino acids. By doing so, you can maximize muscle protein synthesis and maintain a positive muscle protein balance throughout the day, ensuring optimal muscle growth.
The Protein Myth: How Much is Enough?
There seems to be a never-ending debate about how much protein is enough for muscle building. Let’s debunk some common protein myths and shed light on the protein requirements for athletes and bodybuilders.
The Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA)
The Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for protein is the amount considered sufficient to meet the nutritional needs of the average healthy individual. However, the RDA may not necessarily reflect the protein needs of athletes and individuals engaged in intense resistance training. While the RDA ranges between 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight, athletes and bodybuilders may require higher protein intake to support muscle growth and recovery.
Protein Needs for Athletes and Bodybuilders
For athletes and bodybuilders, protein needs are generally higher due to increased muscle breakdown during exercise and the need for muscle repair and growth. The International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) recommends a protein intake range of 1.4 to 2 grams per kilogram of body weight for athletes engaging in resistance training. However, individual variation also plays a role, and factors such as body composition goals and training intensity should be taken into account when determining protein needs.
Individual Variations in Protein Requirements
It’s essential to recognize that individual variations exist when it comes to protein requirements. Some individuals may benefit from higher protein intake, while others may thrive with slightly lower amounts. Factors such as age, sex, body composition, metabolic rate, and training goals can influence protein needs. It’s advisable to work with a qualified nutrition professional to determine an optimal protein intake that suits your specific needs and goals.

Supplements for Muscle Growth
In the pursuit of muscle growth, protein supplements can offer convenience and an extra boost to your protein intake. Let’s explore some popular protein supplements and their potential benefits.
Whey Protein
Whey protein is one of the most popular and widely used protein supplements. It’s derived from milk and contains a high amount of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), particularly leucine. Whey protein is rapidly absorbed by the body, making it an excellent choice for post-workout protein consumption. It’s also rich in essential amino acids and has been shown to enhance muscle protein synthesis, making it a valuable tool for muscle growth.
Casein Protein
Casein protein is another milk-derived protein, but it differs from whey protein in terms of digestion rate. Casein is a slow-digesting protein, resulting in a sustained release of amino acids into the bloodstream. This slow digestion can be advantageous, especially when consumed before bed, as it provides a continuous supply of amino acids during the overnight fast. Casein protein can help prevent muscle breakdown and promote muscle growth during prolonged periods without food intake.
Plant-Based Protein Powders
For those following vegetarian or vegan diets, plant-based protein powders can be a great alternative to animal-derived options. Plant-based protein powders are made from sources such as peas, rice, soy, hemp, and quinoa, which offer a complete amino acid profile. These powders can provide the necessary amino acids for muscle building and are often rich in other beneficial nutrients such as fiber and antioxidants. Plant-based protein powders can be consumed post-workout or throughout the day to support muscle growth in individuals following plant-based diets.
Protein Timing Strategies for Optimal Muscle Growth
Now that we’ve covered the different types of protein supplements, let’s delve into specific protein timing strategies to optimize muscle growth and recovery.
Protein Timing Around Workouts
Consuming protein around your workouts can have a significant impact on muscle protein synthesis and recovery. Aim to consume a protein-rich meal or snack within an hour before your workout to provide your muscles with a readily available source of amino acids. Additionally, post-workout protein intake is crucial to kick-start the muscle repair process and initiate muscle protein synthesis. By timing your protein intake around your workouts, you maximize the benefits of protein for muscle growth.
Protein Timing Before Bed
Consuming protein before bed can be beneficial, especially for those aiming for muscle growth. As mentioned earlier, casein protein is an excellent choice due to its slow digestion rate. By consuming a casein protein shake or a protein-rich snack before bed, you provide your muscles with a prolonged supply of amino acids throughout the night. This can help prevent muscle breakdown and promote muscle protein synthesis during the overnight fasting period.
Protein Timing for Vegetarians and Vegans
Individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets can also benefit from specific protein timing strategies. By spreading their plant-based protein intake throughout the day, vegetarians and vegans provide their muscles with a constant supply of amino acids. Additionally, consuming a protein-rich meal or snack after exercise can help optimize muscle recovery and growth. Plant-based protein supplements, such as those made from pea or soy protein, can be valuable tools for meeting protein requirements and timing protein intake effectively.
Balancing Protein Intake with Other Nutrients
While protein plays a crucial role in muscle building, it’s essential to balance your protein intake with other nutrients to support optimal muscle growth. Let’s explore the roles of carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals in enhancing muscle recovery and overall performance.
Carbohydrates: Fuel for Muscle Building
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for your body, particularly during high-intensity exercise. When you consume carbohydrates, they get stored in your muscles as glycogen, which serves as a readily available fuel source during workouts. By ensuring an adequate intake of carbohydrates, you can support your training performance and prevent muscle breakdown by providing readily available energy.
Fats: Supporting Hormonal Balance
Fats often receive a bad reputation, but they play a crucial role in supporting optimal muscle growth. Fats are vital for hormone production, which is essential for muscle recovery and growth. Including healthy sources of fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and oily fish, in your diet can help maintain hormonal balance and support muscle-building processes.
Vitamins and Minerals: Enhancing Muscle Recovery
Vitamins and minerals are essential for overall health, but they also play a role in muscle recovery and growth. Micronutrients such as vitamin D, magnesium, calcium, and zinc contribute to muscle function and recovery. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources in your diet can help ensure adequate vitamin and mineral intake to support optimal muscle growth.
Side Effects and Risks of Excessive Protein Consumption
While protein is essential for muscle growth, it’s crucial to address potential risks and side effects associated with excessive protein consumption.
Kidney Strain and Dehydration
One concern often raised is that excessive protein intake may strain the kidneys and lead to dehydration. However, research suggests that individuals with healthy kidneys and adequate hydration are unlikely to experience any adverse effects from consuming high-protein diets. It’s essential to balance your protein intake with adequate fluid intake to support overall health and well-being.
Digestive Issues
Consuming large amounts of protein can sometimes lead to digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and stomach discomfort. These symptoms can vary from person to person, so it’s essential to listen to your body and adjust your protein intake accordingly. If you experience digestive issues, consider spreading your protein intake throughout the day and opting for more easily digestible protein sources.
Potential Nutrient Imbalances
Relying excessively on protein supplements or high-protein foods may lead to imbalances in other nutrients. It’s essential to maintain a varied and balanced diet to ensure you receive all the necessary vitamins, minerals, and other macronutrients your body needs for optimal health and muscle growth. Supplementing with protein should be done within the context of a well-rounded diet and not as a replacement for whole foods.
Conclusion
Protein is undoubtedly a vital component in building muscle. It serves as the building blocks for your muscles, stimulates muscle protein synthesis, and supports muscle recovery and growth. By understanding the essential components of protein, the role of amino acids, protein timing strategies, and the importance of protein quality, you can optimize your muscle-building potential. Remember to incorporate a variety of high-quality protein sources into your diet, balance your protein intake with other nutrients, and listen to your body’s individual needs. With the right knowledge and a well-rounded approach, you can fuel your muscle-building journey and achieve the results you desire. Keep pushing yourself, stay consistent, and enjoy the rewarding process of building muscle with the power of protein!
