In this article, you will explore the fascinating world of cholesterol and unravel the mystery behind the distinction between good and bad cholesterol. Discover how understanding this difference can impact your overall health and make informed choices to keep your heart happy and healthy. Let’s dive straight into the different types of cholesterol and uncover their unique characteristics.

Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that is found in all cells of the body. It plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the production of hormones, vitamin D, and digestive substances. However, having high levels of cholesterol in your blood can increase your risk of developing heart disease.
Definition of cholesterol
Cholesterol is a lipid, a type of fat that is produced by the liver and also obtained from certain foods. It is insoluble in blood, so it needs to be transported through the bloodstream by lipoproteins, which are specialized proteins that carry cholesterol in the body.

Types of cholesterol
Cholesterol is generally categorized into two main types: high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
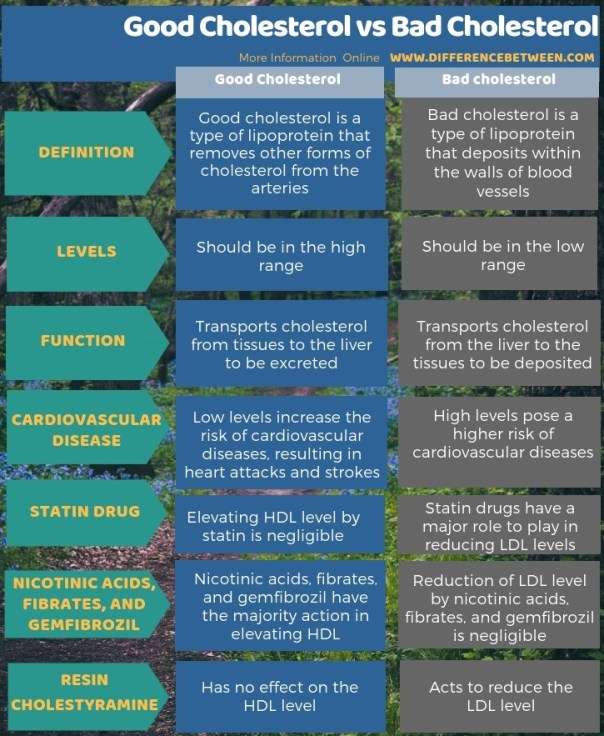
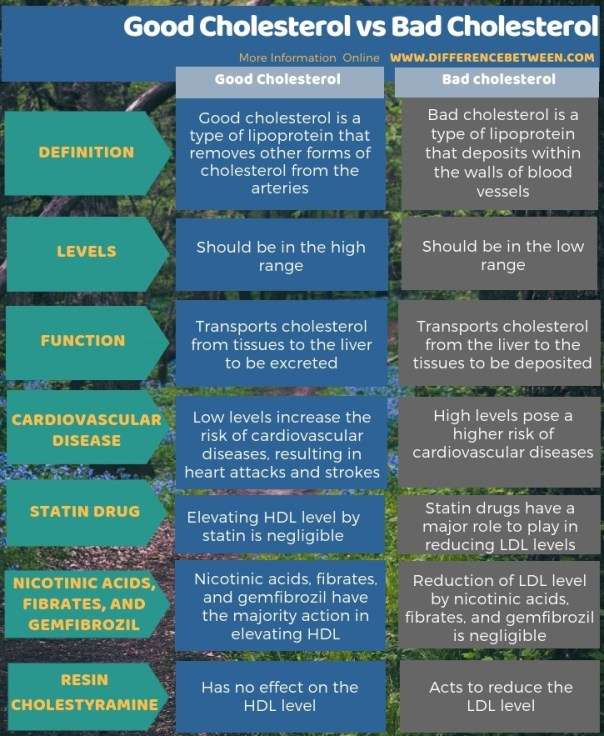
Good Cholesterol (HDL)
HDL cholesterol is often referred to as “good cholesterol” because it has a positive impact on your overall health, especially your heart. HDL cholesterol helps to transport excess cholesterol from the bloodstream back to the liver where it can be eliminated from the body.
Functions of HDL cholesterol
Aside from its role in cholesterol transport, HDL cholesterol also has other functions that benefit your body. It possesses anti-inflammatory properties, helps to maintain the integrity of blood vessels, and aids in the removal of excess cholesterol from arterial walls.
Role in heart health
HDL cholesterol plays a crucial role in maintaining heart health. High levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. It helps to prevent the build-up of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to blockages and ultimately result in heart attacks or strokes.

Bad Cholesterol (LDL)
LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” is responsible for carrying cholesterol to different parts of the body. Unlike HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol can become deposited in the walls of your arteries, leading to the formation of plaque.
Functions of LDL cholesterol
The primary function of LDL cholesterol is to transport cholesterol to the cells that need it for various purposes. However, when the levels of LDL cholesterol are high, it can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the deposition of plaque in the arteries.
Effects on heart health
High levels of LDL cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems. When LDL cholesterol becomes oxidized, it triggers an inflammatory response in the arteries, leading to the accumulation of plaque and narrowing of the blood vessels. This can restrict blood flow and increase the chances of heart attacks or strokes.
Causes and Risk Factors
The levels of cholesterol in your body can be influenced by various factors, including genetic, dietary, and lifestyle factors.
Genetic factors
Genetics play a role in determining your cholesterol levels. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition towards higher levels of cholesterol, making them more susceptible to developing high levels of bad cholesterol.
Dietary factors
Your diet plays a significant role in your cholesterol levels. Consuming foods that are high in saturated and trans fats can raise the levels of LDL cholesterol in your blood. Additionally, a diet that is low in fiber can also contribute to higher cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle factors
Certain lifestyle choices can impact your cholesterol levels. Lack of physical activity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and being overweight or obese can all contribute to higher levels of bad cholesterol.
Effects on Cardiovascular Health
The role of cholesterol in atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the build-up of plaque in the arteries, is well-established.
The role of cholesterol in atherosclerosis
In atherosclerosis, LDL cholesterol becomes oxidized and triggers an inflammatory response in the artery walls. This leads to the accumulation of fatty deposits or plaque, which can narrow the arteries and restrict blood flow.
Correlation with heart disease
High levels of LDL cholesterol have been strongly associated with an increased risk of heart disease. When the arteries become narrowed due to the build-up of plaque, blood flow to the heart becomes limited, increasing the chances of a heart attack or other cardiovascular events.
Measuring and Interpreting Cholesterol Levels
Monitoring your cholesterol levels is crucial for understanding your risk of developing heart disease. Cholesterol levels are typically measured through a blood test, and various components are evaluated.
Total cholesterol
Total cholesterol is a measure of both HDL and LDL cholesterol in your blood. It provides an overall indication of your cholesterol levels.
HDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol levels should be higher because of its beneficial effects. A higher level of HDL cholesterol is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease.
LDL cholesterol
LDL cholesterol levels should be lower since high levels of LDL cholesterol are linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are another type of fat found in the blood. High levels of triglycerides can also contribute to the development of heart disease.
Recommended levels
The American Heart Association recommends the following cholesterol level targets:
- Total cholesterol: Less than 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
- HDL cholesterol: Above 60 mg/dL
- LDL cholesterol: Below 100 mg/dL
- Triglycerides: Below 150 mg/dL
Managing Cholesterol Levels
Controlling your cholesterol levels is essential for maintaining good heart health. Adopting certain lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication can help manage cholesterol levels effectively.
Dietary changes
Making dietary changes is a crucial aspect of managing cholesterol levels. A heart-healthy diet should be low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. Instead, focus on consuming foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Physical activity
Regular physical activity contributes to higher levels of HDL cholesterol and overall heart health. Engaging in aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can help raise HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL cholesterol.
Medication options
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient in managing cholesterol levels. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications, such as statins, to help lower LDL cholesterol. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and discuss any concerns or side effects.
Dietary Guidelines for Maintaining Healthy Cholesterol
Adopting a heart-healthy diet can have a significant impact on your cholesterol levels. Here are some dietary guidelines to help maintain healthy cholesterol levels:
Dietary fat recommendations
Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, which are found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, processed snacks, and fried foods. Instead, opt for healthier fats, such as monounsaturated fats found in olive oil and avocados, and polyunsaturated fats found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
Foods to avoid
Avoid or limit consumption of foods high in cholesterol, such as organ meats, shellfish, and egg yolks. Additionally, minimize your intake of foods high in sodium and added sugars, as they can contribute to higher cholesterol levels.
Foods to include
Incorporate foods that are rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, legumes, and fruits, as they can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Include fatty fish, like salmon and mackerel, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids that can help increase HDL cholesterol levels.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing high cholesterol and its associated heart health risks involves adopting certain strategies to maintain overall well-being.
Lifestyle modifications
Making healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce your risk of developing high cholesterol. Maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, avoid smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and manage stress levels.
Regular health screenings
Regular health screenings, including cholesterol level checks, can identify any abnormalities or potential risks early on. It is recommended to have cholesterol levels checked at least once every five years for individuals aged 20 years and older.
Controlling other risk factors
Some risk factors, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, can contribute to higher cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Controlling these conditions through medication, lifestyle changes, or both can help manage cholesterol levels effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding cholesterol and its impact on heart health is vital for maintaining overall wellness. By recognizing the differences between good and bad cholesterol, as well as the causes and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to manage and maintain healthy cholesterol levels. By adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and monitoring your cholesterol levels regularly, you can reduce the risk of heart disease and lead a healthier life. Remember, a well-informed and proactive approach is the key to maintaining optimal heart health.