So, have you ever heard of intermittent fasting? It seems like everyone is talking about it these days. It’s become quite the popular trend in the health and wellness world, but what exactly is it? Well, let me break it down for you. Intermittent fasting is a way of eating that involves alternating periods of fasting and eating. It’s not really a diet, but more of an eating pattern. And it’s been said to have some pretty amazing benefits for your body and overall health.
So, how does intermittent fasting actually work? Well, there are different methods you can try, but the basic idea is to restrict your calorie intake for certain periods of time. One popular method is the 16/8 method, where you fast for 16 hours and have an 8-hour eating window. Some people prefer to do it every day, while others choose to do it a few times a week. The great thing about intermittent fasting is that you can tailor it to your own lifestyle and preferences.
Now, you might be wondering, why would anyone willingly choose to go without food for an extended period of time? Well, besides the potential weight loss benefits, there are actually a number of health benefits associated with intermittent fasting. It has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation in the body, and even improve brain function. Plus, it can be a way to give your digestive system a break and allow your body to repair and regenerate.
So, if you’re curious to learn more about intermittent fasting and how it can benefit your health, stick around. In our upcoming article, we’ll dive deeper into the different methods of intermittent fasting, the science behind it, and some tips for getting started. Trust me, you won’t want to miss it!
What Is Intermittent Fasting
Definition of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) refers to an eating pattern that alternates between periods of fasting and periods of eating. Unlike traditional diets that focus on what foods to eat, intermittent fasting focuses on when to eat. It is not a diet but a pattern of eating that has gained popularity for its potential health benefits.
During fasting periods, you abstain from consuming calories, allowing your body to enter a fasting state. This usually lasts for a set number of hours, typically 16 to 24 hours, although shorter and longer fasting periods are also practiced.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting has gained attention for its numerous potential benefits:
-
Weight Loss: Intermittent fasting can be an effective strategy for weight loss. By restricting the time available for eating, you naturally consume fewer calories. Additionally, fasting can increase your metabolic rate and fat oxidation, facilitating weight loss.
-
Health Improvements: Studies have shown that intermittent fasting may improve various aspects of health, such as reducing inflammation, improving insulin sensitivity, and lowering blood pressure. These health improvements can lead to a decreased risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
-
Hormonal Regulation: Intermittent fasting has been found to affect the production and regulation of hormones in the body. It can increase the secretion of human growth hormone (HGH), which aids in muscle growth, fat loss, and overall metabolism. Fasting also enhances insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
-
Longevity: Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may promote longevity and increase lifespan. Caloric restriction, which is similar to fasting, has been shown to extend lifespan in various organisms. While the mechanisms behind this effect are not fully understood, it is believed that fasting triggers cellular repair and stress resistance pathways that contribute to longevity.
-
Mental Clarity: Many people who practice intermittent fasting report improved mental clarity and focus. This may be attributed to increased production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that promotes the growth and maintenance of brain cells. Fasting also enhances autophagy, a cellular process that clears damaged cells from the brain, potentially improving cognitive function.
Different Types of Intermittent Fasting
There are several popular methods of intermittent fasting, each with its own unique approach to fasting and eating windows:
-
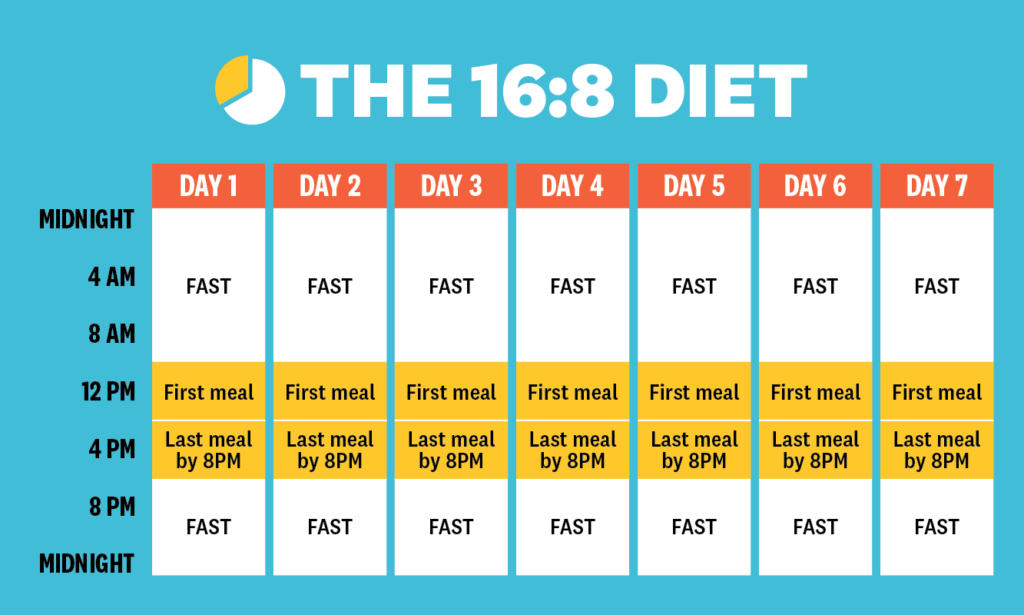
16/8 Method: This method involves fasting for 16 hours every day and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. For example, you might have your first meal at 12 pm and your last meal at 8 pm. This method is convenient for many people as it can be easily incorporated into their daily routine.
-
5:2 Diet: The 5:2 diet involves eating normally for 5 days of the week and restricting calorie intake to 500-600 calories for the remaining 2 days. These fasting days do not have to be consecutive and can be spread throughout the week.
-
Alternate-Day Fasting: As the name suggests, this method involves fasting every other day. On fasting days, you consume little to no calories, while on non-fasting days, you can eat freely. This approach can be more challenging for some individuals, as it involves long periods of complete fasting.
-
24-Hour Fasting: This method entails fasting for a complete 24 hours once or twice a week. For example, you might eat dinner one day and then fast until dinner the next day. During the fasting period, you can consume non-caloric beverages such as water, tea, or coffee.
Intermittent Fasting and Weight Loss
One of the primary reasons people turn to intermittent fasting is for weight loss. By restricting the time available for eating, you naturally consume fewer calories, leading to a calorie deficit and subsequent weight loss. Moreover, fasting can increase fat oxidation and boost your metabolic rate, further aiding weight loss efforts.
Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can be just as effective as traditional calorie-restricted diets for weight loss. It may also help preserve muscle mass during weight loss, which is beneficial for long-term weight maintenance.
Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health
Beyond weight loss, intermittent fasting has been associated with various health benefits. Research suggests that intermittent fasting may improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and lower blood pressure, all of which can contribute to better overall health.
Intermittent fasting has been found to enhance the body’s ability to utilize glucose, resulting in improved blood sugar control. This is particularly important for individuals with insulin resistance or pre-diabetes, as it can help prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Moreover, intermittent fasting has been shown to reduce markers of inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. By reducing inflammation, intermittent fasting may help protect against these conditions.
Intermittent Fasting and Hormonal Regulation
Intermittent fasting has a profound impact on the regulation of hormones in the body. During fasting periods, the body experiences hormonal changes that can have positive effects on metabolism and overall health.
One hormone affected by intermittent fasting is insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. Fasting improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to utilize glucose more efficiently. This can reduce the risk of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Another hormone influenced by fasting is human growth hormone (HGH). Fasting can increase HGH levels in the body, leading to various benefits such as increased fat burning, muscle growth, and improved metabolism. These effects can contribute to weight loss and overall body composition.
Intermittent Fasting and Longevity
Intermittent fasting has been linked to longevity and increased lifespan in various organisms. While the exact mechanisms behind this association are not fully understood, it is believed that the cellular repair and stress resistance pathways activated during fasting contribute to these effects.
Fasting triggers a process called autophagy, in which damaged and dysfunctional cells are cleared and recycled. This cellular cleansing has been shown to have anti-aging effects and may reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
Additionally, intermittent fasting reduces oxidative stress, which is thought to play a major role in aging and disease development. By reducing oxidative stress and promoting cellular repair, fasting may contribute to a longer and healthier life.
Intermittent Fasting and Mental Clarity
Many individuals who practice intermittent fasting report improved mental clarity and focus. This is thought to be due to increased production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that promotes the growth and maintenance of brain cells.
Intermittent fasting also enhances autophagy in the brain, clearing out damaged cells and protein buildup that can impair cognitive function. This cellular renewal may improve memory, attention, and overall brain health.
Moreover, fasting has been shown to increase the production of ketone bodies, which are an alternative fuel source for the brain. Ketones have been associated with improved cognitive function and may provide a steady source of energy for the brain during fasting periods.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting is a flexible and accessible approach to eating that has gained popularity for its potential health benefits. It can aid in weight loss, improve health markers, regulate hormones, promote longevity, and enhance mental clarity. With various methods to choose from, individuals can find an intermittent fasting schedule that fits their lifestyle and goals. However, as with any dietary change, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting intermittent fasting to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your individual needs.

